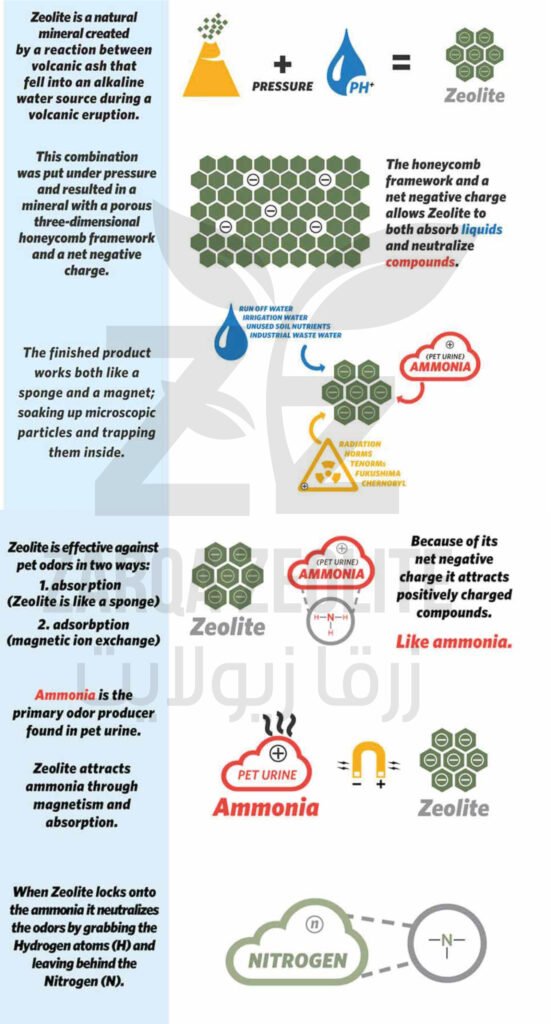
Zeolite is a type of natural mineral and rock, formed by the decomposition of volcanic rocks and their interaction with alkaline waters. It forms unique crystals in shape and properties from aluminum silicates, known as “molecular sieves.” These minerals are characterized by a low specific gravity, due to the presence of voids that constitute 35% to 50% of the crystal volume. Zeolite has a three-dimensional lattice structure resembling honeycomb, composed of layers with interconnected channels and voids where positive ions and water molecules are concentrated.
The ions within the zeolite structure can be easily exchanged with nutrients without affecting their composition, a property known as Cation Exchange Capacity. Water molecules can also be lost and gained with the same ease, giving zeolite its hydration and dehydration properties.